CrowdSec WAF QuickStart for NPMplus
Objectives
The goal of this quickstart is to set up the AppSec Component to safeguard web applications running on NPMplus, an enhanced version of Nginx Proxy Manager.
We'll deploy a set of rules designed to block well-known attacks and currently exploited vulnerabilities.
Additionally, we'll show how to monitor these alerts through the Console.
Prerequisites
-
If you're new to the AppSec Component or Web Application Firewalls, start with the Introduction for a better understanding.
-
It's assumed that you have:
- Docker and Docker Compose installed and ready
- Ports available: 80/TCP, 443/TCP, 443/UDP (exposed to internet), 81/TCP (admin interface, can be internal)
- A text editor (e.g., nano, vim) and a way to download files (e.g., curl)
AppSec Component Setup
Collection installation
To begin setting up the AppSec Component, the initial step is to install a relevant set of rules.
We will utilize the crowdsecurity/appsec-virtual-patching collection, which offers a wide range of rules aimed at identifying and preventing the exploitation of known vulnerabilities.
This collection is regularly updated to include protection against newly discovered vulnerabilities. Upon installation, it receives automatic daily updates to ensure your protection is always current.
We also install the crowdsecurity/appsec-generic-rules collection. This collection contains detection scenarios for generic attack vectors. It provides protection in cases where specific scenarios for vulnerabilities do not exist yet.
Setup the Acquisition
NPMplus provides a Docker Compose file that includes both NPMplus and CrowdSec services. We need to configure the acquisition for AppSec and NPMplus log parsing.
The AppSec part of this file is the AppSec acquisition datasource (source: appsec). For the complete reference of available keys, see the AppSec datasource.
Steps:
- Download the compose.yaml file:
curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ZoeyVid/NPMplus/refs/heads/develop/compose.yaml -o compose.yaml
-
Edit the
compose.yamlfile with your preferred text editor:-
For the NPMplus service: Set the environment variables:
TZ: Your timezone (e.g.,TZ=Europe/Berlin)ACME_EMAIL: Your email address for Let's Encrypt (e.g.,ACME_EMAIL=admin@example.org)LOGROTATE: Set totrue(uncomment this line). This is required for CrowdSec to parse NPMplus logs.
-
For the CrowdSec service: Uncomment the
crowdsecservice block. Make sure to keep theopenappsecline commented (note:appsecandopenappsecare different things).
-
-
Create the acquisition directory and configuration file:
The exact path depends on how volumes are mounted in your
compose.yaml. Typically, you'll need to create the file in the location where CrowdSec's configuration is persisted. If the compose file mounts/opt/crowdsecor/etc/crowdsecfrom the host, create the directory and file there:
# Adjust the path based on your Docker volume mounts
mkdir -p /opt/crowdsec/conf/acquis.d
Alternatively, if you're using a different volume mount path, adjust accordingly. You can also create the file directly inside the container:
docker exec -it crowdsec mkdir -p /etc/crowdsec/acquis.d
- Create the acquisition configuration file
/opt/crowdsec/conf/acquis.d/npmplus.yaml(or/etc/crowdsec/acquis.d/npmplus.yamlif using the container path) with the following content:
filenames:
- /opt/npmplus/nginx/*.log
labels:
type: npmplus
---
filenames:
- /opt/npmplus/nginx/*.log
labels:
type: modsecurity
---
listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:7422
appsec_configs:
- crowdsecurity/appsec-default
name: appsec
source: appsec
labels:
type: appsec
Configuration explained:
- The first two sections configure log parsing for NPMplus logs
- The third section configures the AppSec Component:
listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:7422: The AppSec Component listens on all interfaces on port 7422 (needed for Docker networking)appsec_configs: Uses the AppSec configuration(s) from the installed collectionssource: appsec: Identifies this as an AppSec data source
Running NPMplus and CrowdSec
Start the services using Docker Compose:
docker compose up -d
Install AppSec Collections
After the containers have started, install the required AppSec collections inside the CrowdSec container:
docker exec crowdsec cscli collections install crowdsecurity/appsec-virtual-patching crowdsecurity/appsec-generic-rules
This command installs the following items:
- The AppSec Rules contain the definition of malicious requests to be matched and stopped
- The AppSec Configuration links together a set of rules to provide a coherent set
- The CrowdSec Parser and CrowdSec Scenario(s) are used to detect and remediate persistent attacks
After installing the collections, restart the CrowdSec container to load the new configuration:
docker restart crowdsec
Remediation Component Setup
Now we need to configure NPMplus to function as a Remediation Component for the Security Engine and enable the AppSec Component.
Generate API Key
Generate an API key for NPMplus:
docker exec crowdsec cscli bouncers add npmplus -o raw
Copy the output API key - you'll need it in the next step.
Configure NPMplus
Edit the NPMplus CrowdSec configuration file:
# The file location may vary depending on your Docker setup
# Typically it's at: /opt/npmplus/crowdsec/crowdsec.conf
In this file, you need to:
- Set
ENABLED=trueto enable the CrowdSec integration - Set
API_KEYto the key you generated in the previous step
The configuration file should look similar to:
ENABLED=true
API_KEY=your-api-key-here
Restart NPMplus
Restart the NPMplus container to apply the changes:
docker restart npmplus
Verify Connection
Check the Docker logs to confirm NPMplus is connected to CrowdSec:
docker logs npmplus
You should see lines mentioning that NPMplus is connected to CrowdSec.
Testing the AppSec Component + Remediation Component
If you try to access http://localhost/.env (or your server's IP address) from a browser, your request will be blocked, resulting in the display of the following HTML page:
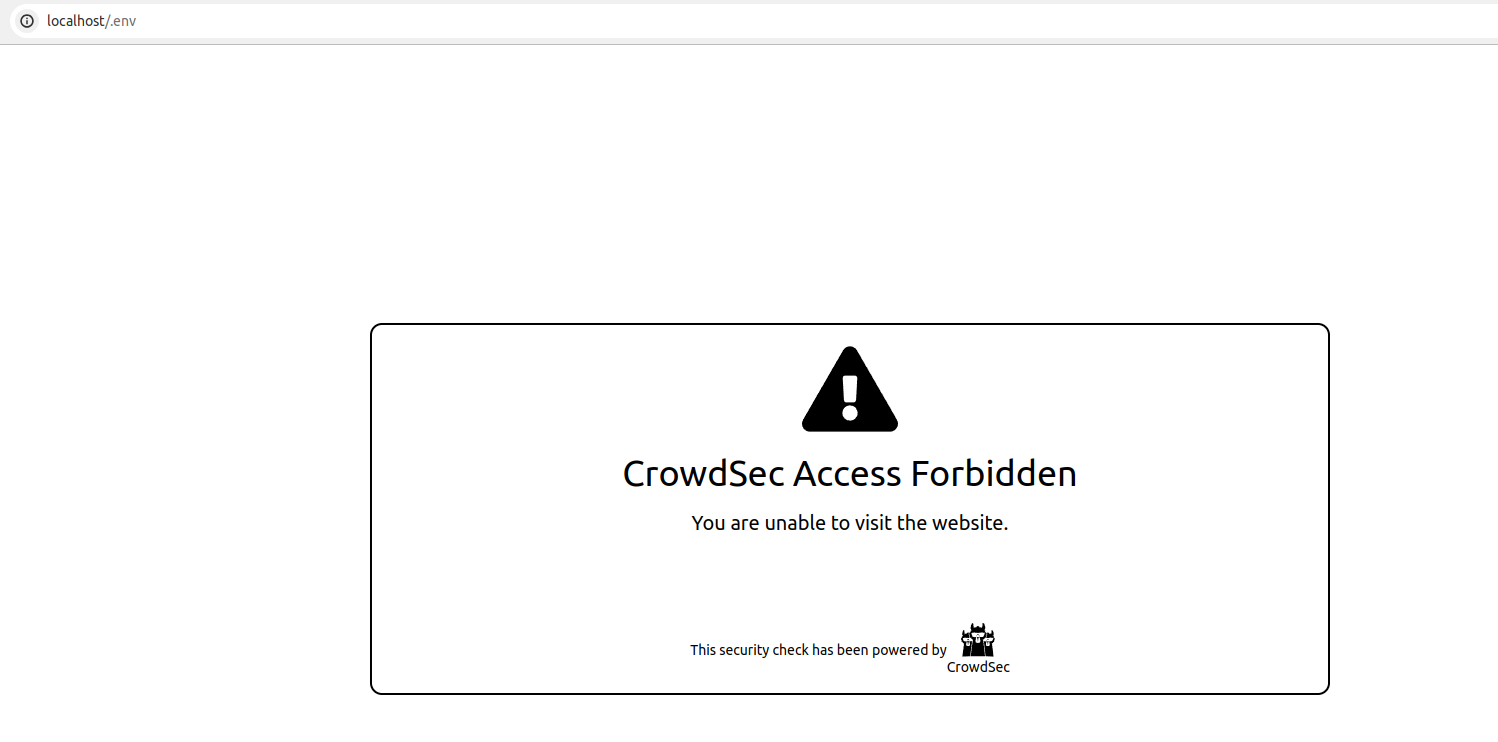
We can also look at the metrics from cscli metrics show appsec - it will display:
- the number of requests processed by the AppSec Component
- Individual rule matches
Example Output
Appsec Metrics:
╭─────────────────┬───────────┬─────────╮
│ Appsec Engine │ Processed │ Blocked │
├─────────────────┼───────────┼─────────┤
│ 0.0.0.0:7422/ │ 2 │ 1 │
╰─────────────────┴───────────┴─────────╯
Appsec '0.0.0.0:7422/' Rules Metrics:
╭─────────────────────────────────┬───────────╮
│ Rule ID │ Triggered │
├─────────────────────────────────┼─────────┤
│ crowdsecurity/vpatch-env-access │ 1 │
╰─────────────────────────────────┴───────────╯
You can test and investigate further with Stack Health-Check and Appsec Troubleshooting guide
Explanation
What happened in the test that we just did is:
- We did a request (
localhost/.env) to our web server - Thanks to the NPMplus Remediation Component configuration, the request was forwarded to
http://crowdsec:7422(or the appropriate Docker network address) - Our AppSec Component, listening on
0.0.0.0:7422analyzed the request - The request matches the AppSec rule to detect .env access
- The AppSec Component thus answered with HTTP 403 to the Remediation Component, indicating that the request must be blocked
- The web server then presented us with the default "request blocked" page.
Integration with the Console
If you haven't yet, follow the guide about how to enroll your Security Engine in the Console.
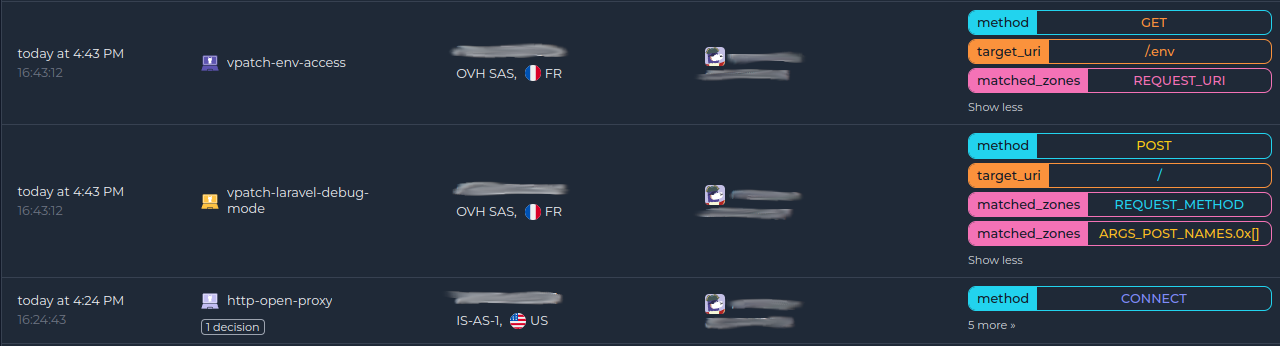
Once done, all your alerts, including the ones generated by the AppSec Component, appear in the Console:
Next steps
You are now running the AppSec Component on your CrowdSec Security Engine with NPMplus, congrats!
As the next steps, you can:
- Look at WAF Deployment Strategies to discover how to gradually improve your WAF security.
- Look at the Rules syntax and creation process to create your own and contribute
- Take a look at the benchmarks

