Troubleshooting Security Engine
Community support
Please try to resolve your issue by reading the documentation. If you're unable to find a solution, don't hesitate to seek assistance in:
Health
How to check the status
- Linux/Freebsd
- Windows
- Kubernetes
sudo systemctl status crowdsec
Get-Service crowdsec
kubectl get pods -n crowdsec
How to check if CAPI is reachable
cscli capi status
Example output
time="2024-01-08 14:08:20" level=info msg="Loaded credentials from /etc/crowdsec/online_api_credentials.yaml"
time="2024-01-08 14:08:20" level=info msg="Trying to authenticate with username XXXXXXXXXXX on https://api.crowdsec.net/"
time="2024-01-08 14:08:22" level=info msg="You can successfully interact with Central API (CAPI)"
How do I know if my setup is working correctly? Are some unparsed logs normal?
Yes, Security Engine parsers only parse the logs that are relevant for scenarios.
Take a look at cscli metrics and understand what do they mean to know if your setup is correct.
You can take an extra step and use cscli explain to understand what log lines are parsed, and how:
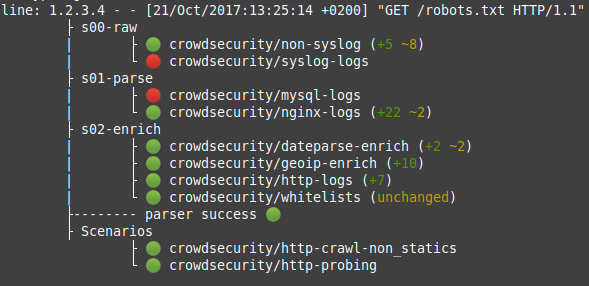
Why are some logs not parsed in cscli metrics?
If logs do not seem to be parsed correctly, use cscli explain:
# cscli explain --log "May 16 07:50:30 sd-126005 sshd[10041]: Invalid user git from 78.142.18.204 port 47738" --type syslog
line: May 16 07:50:30 sd-126005 sshd[10041]: Invalid user git from 78.142.18.204 port 47738
├ s00-raw
| └ 🟢 crowdsecurity/syslog-logs (first_parser)
├ s01-parse
| ├ 🔴 crowdsecurity/iptables-logs
| ├ 🔴 crowdsecurity/mysql-logs
| ├ 🔴 crowdsecurity/nginx-logs
| └ 🟢 crowdsecurity/sshd-logs (+6 ~1)
├ s02-enrich
| ├ 🟢 crowdsecurity/dateparse-enrich (+2 ~1)
| ├ 🟢 crowdsecurity/geoip-enrich (+13)
| ├ 🔴 crowdsecurity/http-logs
| └ 🟢 crowdsecurity/whitelists (unchanged)
├-------- parser success 🟢
├ Scenarios
├ 🟢 crowdsecurity/ssh-bf
├ 🟢 crowdsecurity/ssh-bf_user-enum
├ 🟢 crowdsecurity/ssh-slow-bf
└ 🟢 crowdsecurity/ssh-slow-bf_user-enum
This command shows how each parser behaves.
I want to add collection X: how do I add log files and test that it works?
When adding a collection to your setup, the hub will usually specify log files to add.
Decisions
How to list current decisions
cscli decisions list
Additional filtering is possible please read cscli decisions list for more information.
How to remove a decision on an IP
cscli decisions delete -i x.x.x.x
Additional filtering is possible please read cscli decisions delete for more information.
How to control granularity of decisions
The Security Engine is designed to be as flexible as possible, and allows you to control the granularity of decisions.
Profiles allows you to control which decision will be applied to which alert.
How to add whitelists or prevent the Security Engine from banning a given IP
Recommended ways to prevent a specific IP from being banned:
- Use Centralized AllowLists - Works on local decisions, blocklists and can be controlled from the Console.
- Parser Whitelists - Applies directly on the log parsing pipeline.
I need to whitelist an event pattern instead of a single IP address
You can exclude specific events using whitelist parsers. It can discard events based on a specific URL, source IP address, or any other condition.
Scenarios
Why are some scenarios/parsers "tainted" or "custom"?
When using cscli to list your parsers, scenarios, and collections, some might appear as "tainted" or "local".
"tainted" items:
- Originate from the hub
- Were locally modified
- Will not be automatically updated/upgraded by
csclioperations (unless--forceor similar is specified) - Won't be sent to Central API and won't appear in the Console (unless
cscli console enable taintedhas been specified)
"local" items:
- Have been locally created by the user
- Are not managed by
csclioperations - Won't be sent to Central API and won't appear in the Console (unless
cscli console enable customhas been specified)
Scenario X keeps triggering, it's a false trigger
To avoid false positives from a known scenario, you can use:
- Parser Whitelists - Applies directly on the log parsing pipeline.
Set a custom/tainted scenario in simulation mode
If you want to set a custom/tainted scenario in simulation mode, you need to provide the scenario's filename instead of its name.
For example, you have a scenario called crowdsecurity/my-custom-scenario located in {config_dir}/scenarios/my_custom_scenario.yaml.
To enable the simulation mode for this scenario, run:
- Linux/Freebsd
- Windows
- Kubernetes
sudo cscli simulation enable my_custom_scenario.yaml
cscli.exe simulation enable my_custom_scenario.yaml
kubectl exec -it crowdsec-agent-* -n crowdsec -- cscli simulation enable my_custom_scenario.yaml
My scenario is triggered with less logs than the scenario capacity
When you install CrowdSec, the CrowdSec Wizard runs automatically to find and add basic log files to the acquisition configuration. If you run the 'wizard.sh' script again after installing and you have common log files, they might be added multiple times to your acquisition configuration. This causes CrowdSec to read each log line as many times as the file is configured in the acquisition settings.
Please review your acquisition files and remove any duplicate log entries.
Is scenario X working on my logs?
To test if logs are correctly parsed and checked by scenarios, use:
- Replay mode allows you to process cold logs and see scenarios triggered.
cscli explainallows you to inspect the parsing process for one or more log lines.
Configuration
Where is configuration stored?
Where is data stored?
CrowdSec stores its data in /var/lib/crowdsec/data/ folder for UNIX and C:\ProgramData\CrowdSec\data\ for Windows.
This is where the default sqlite database and data files needed for scenarios are kept.
Which databases does the Security Engine support and how to switch?
Security Engine supports SQLite (default), MySQL, and PostgreSQL databases. See databases configuration for relevant configuration. Thanks to the Local API, distributed architectures are resolved even with sqlite database.
Multi-server setup
For multi-server setups, use one of the following:
Logs
Where are the logs stored?
By default CrowdSec will log to the following locations depending on platform:
- Linux
/var/log/crowdsec.log - Freebsd
/var/log/crowdsec.log- Opnsense
/var/log/crowdsec/crowdsec.log - Pfsense
/var/log/crowdsec/crowdsec.log
- Opnsense
- Windows
C:\ProgramData\CrowdSec\log\crowdsec.log - Kubernetes
kubectl logs -n crowdsec crowdsec-(agent|lapi)-*
These are the default log locations. Third-party integrations may use different paths.
Filtering logs to only show errors
Use OS-specific commands to filter logs and show only errors.
- Linux/Freebsd
- Windows
- Kubernetes
sudo grep -E "level=(error|fatal)" /var/log/crowdsec.log
- Powershell
- CMD
Select-String "level=(error|fatal)" C:\ProgramData\CrowdSec\log\crowdsec.log
findstr "level=error level=fatal" C:\ProgramData\CrowdSec\log\crowdsec.log
kubectl logs -n crowdsec crowdsec-agent-* | grep -E "level=(error|fatal)"
Please make sure the log location matches your distribution.
Common Errors
Cannot bind to the configured port or IP
- error message might look like:
level=fatal msg="while serving local API: listen tcp 127.0.0.1:8080: bind: address already in use"
- solution verify another service is not already using the port or ip address + port combination. If it is, you can edit the
listen_uriin the configuration fileconfig.yamland updatelocal_api_credentials.yamlto the same value. Then you can restart CrowdSec withsudo systemctl restart crowdsec.
Cannot authenticate to the local API
- error message might look like:
level=fatal msg="starting outputs error : authenticate watcher (fcb7303c4df44c03ada289dd7ec3dbe7cU3GaseSWdqUaVg6): API error: ent: machine not found"
- solution regenerate the credentials via cscli machines command. If the local API is on the same machine you can run
sudo cscli machines add -a(-awill automatically generate a random machine name and password). Then you can restart CrowdSec withsudo systemctl restart crowdsec.
Cannot connect to the local API
- error message might look like:
level=error msg="error while performing request: dial tcp 127.0.0.1:8080: connect: connection refused; 4 retries left"
- solution verify that the local API runs on the logged IP and port. If the logged IP and port is incorrect, you can update
/etc/crowdsec/local_api_credentials.yamlto the correct IP and port (If local API is running on the same machine you can rungrep listen_uri /etc/crowdsec/config.yamlto find it). Then you can restart CrowdSec withsudo systemctl restart crowdsec. If the logged IP and port is correct, verify that the local API is running viasudo systemctl status crowdsec.
Cannot start because of an invalid configuration file
- error message might look like:
level=fatal msg="/etc/crowdsec/config.yaml: yaml: unmarshal errors:\n line 1: field test not found in type csconfig.Config"
- solution CrowdSec will inform you which field or line is invalid. You can edit the configuration file and fix the error. Then you can restart CrowdSec with
sudo systemctl restart crowdsec. If you are unsure what the configuration file should look like you can find the default configuration files here or examples via the documentation.
General Questions
How to report a bug
To report a bug, open an issue on the affected component repository:
What license is provided?
The Security Engine and Remediation Components are provided under the MIT license.
What is CrowdSec Security Engine?
CrowdSec Security Engine is open-source security software. See the overview.
What language is it written in?
CrowdSec Security Engine is written in Golang.
What resources are needed to run Security Engine?
Security Engine itself is rather light, and in a small to medium setup should use less than 100Mb of memory.
During intensive logs processing, CPU is going to be the most used resource, and memory should grow slightly.
How fast is it
The Security Engine can easily handle several thousands of events per second on a rich pipeline (multiple parsers, geoip enrichment, scenarios and so on). Logs are a good fit for sharding by default, so it is definitely the way to go if you need to handle higher throughput.
If you need help with large-scale deployment, please contact us through this form.
What is the performance impact?
As the Security Engine only works on logs, it shouldn't impact your production. When it comes to remediation components, please refer to their documentation.
Which information is sent to your services?
See CAPI documentation.
How to set up a proxy
Setting up a proxy works out of the box, the net/http golang library can handle those environment variables:
HTTP_PROXYHTTPS_PROXYNO_PROXY
For example:
export HTTP_PROXY=http://<proxy_url>:<proxy_port>
Systemd variable
On Systemd devices you have to set the proxy variable in the environment section for the CrowdSec service. To avoid overwriting the service file during an update, a folder is created in /etc/systemd/system/crowdsec.service.d and a file in it named http-proxy.conf. The content for this file should look something like this:
[Service]
Environment=HTTP_PROXY=http://myawesomeproxy.com:8080
Environment=HTTPS_PROXY=https://myawesomeproxy.com:443
Environment=NO_PROXY=127.0.0.1,localhost,0.0.0.0
After this change you need to reload the systemd daemon using:
systemctl daemon-reload
Then you can restart CrowdSec like this:
systemctl restart crowdsec
Sudo
If you use sudo cscli, just add this line in visudo after setting up the previous environment variables:
Defaults env_keep += "HTTP_PROXY HTTPS_PROXY NO_PROXY"
Tor
You can configure cscli and crowdsec to use tor to anonymously interact with our API.
All (http) requests made to the central API to go through the tor network.
With tor installed, setting HTTP_PROXY and HTTPS_PROXY environment variables to your socks5 proxy, as well as setting NO_PROXY to local addresses to prevent LAPI errors, will do the trick.
Edit crowdsec systemd unit to push/pull via tor
[Service]
Environment="HTTPS_PROXY=socks5://127.0.0.1:9050"
Environment="HTTP_PROXY=socks5://127.0.0.1:9050"
Environment="NO_PROXY=127.0.0.1,localhost,0.0.0.0"
Running the wizard with tor
$ sudo HTTPS_PROXY=socks5://127.0.0.1:9050 HTTP_PROXY=socks5://127.0.0.1:9050 NO_PROXY=127.0.0.1,localhost,0.0.0.0 ./wizard.sh --bininstall
cscli
$ sudo HTTP_PROXY=socks5://127.0.0.1:9050 HTTPS_PROXY=socks5://127.0.0.1:9050 NO_PROXY=127.0.0.1,localhost,0.0.0.0 cscli capi register
How to disable the central API
To disable the central API, simply comment out the online_client section of the configuration file.

